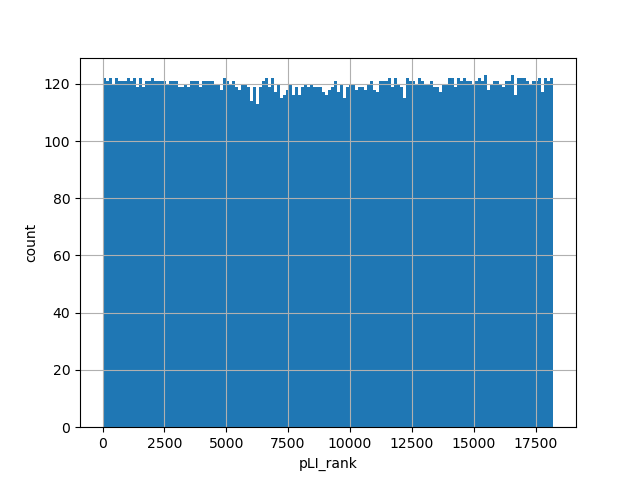
Probability of Loss-of-Function Intolerance
Small values desc: less likely to be Loss-of-function intolerant
Large values desc: more likely to be Loss-of-function intolerant
Gene rank after sorting by pLI intolerance score
Small values desc: more likely to be Loss-of-function intolerant
Large values desc: less likely to be Loss-of-function intolerant